What is 3D Printing? Why should we use 3D printing?
3D printing, or Additive Manufacturing, is a way of creating three dimensional objects for various purposes, by melting a long string of material and adding it together, plastic being the most common one, into a desirable shape. 3D printers are used by people working in various fields, such as manufacturers, medics, engineers, but also a large number of hobbyists.
The main advantage of 3D printers is the possibility of minimizing the usage of raw material, as the layer-by-layer construction means having no need of cutting additional pieces of the final product.
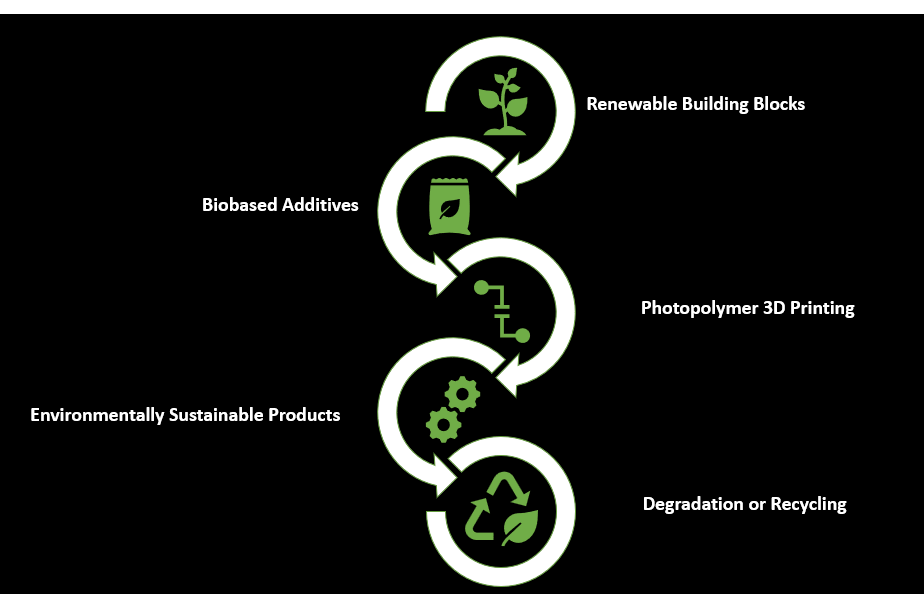
How can 3D Printing be environmentally sustainable?
Bioplastics – What are they?
Bioplastics are plastic materials produced from renewable biomass sources, such as vegetable fats and oils, corn starch, straw, woodchips, sawdust or recycled food waste. Some bioplastics are obtained by processing directly from natural biopolymers including polysaccharides (starch or cellulose) and proteins (soy protein, gluten and gelatin), while others are chemically synthesised from sugar derivatives and lipids. In contrast, common plastics are derived from petroleum or natural gas
How can they help the environment?
One advantage of bioplastics is their independence from fossil fuel as a crucial material, which is a finite and volatile product. Bioplastics can be made with a lower carbon footprint than their fossil counterparts, for example when biomass is used as raw material and also for energy production.
A sustainable ecological footprint can be accomplished in two ways:
Firstly, the use of bioplastics, plant-based raw materials, has the advantage of being renewable, capturing the CO2 present in the air, at the same time, participating in the reduction of the greenhouse effect. The main bioplastic that would have the most benefits as a source for 3D Printing is Nylon PA11, created from renewable castor oil. Subtypes of this material have different useful properties:
- PA11 ESD, with the advantage of having electrostatic discharging properties for increased process safety in advanced applications, especially in the electronics sector
- PA11 CF, one of the strongest materials in the 3D printing industry, combining high ductility and impact performance as well as really high rigidity
- PA11 SLS & PA11 MJF, offering impact strength, used in the making of durable parts, able to withstand high mechanical loads and stress
A few applications of PA11
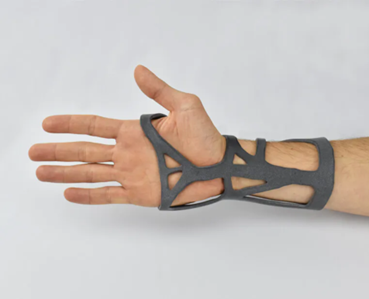


This material is resistant and approved for skin contact, thus it is used to make orthopedic parts PA11 has good impact resistance, being used in manufacturing interior car components It can withstand high mechanical loads and stress, making a good solution for the manufacturing of living hinges -
 Sustainability can also be achieved by using biodegradable filaments, such as PVA, or Polyvinyl Alcohol, a soft and biodegradable polymer that is highly sensitive to moisture. When exposed to water, PVA will dissolve, which makes it a very useful support structure material for 3D printing. When printing extremely complex shapes or ones with partially enclosed cavities, PVA supports can be used and easily removed by dissolving in warm water. Standard supports may have been difficult to print or remove in these situations. PVA can also be used as a model material if there is a need to make quick prototypes, with the end-goal of not wasting or polluting, such as in the case of ordinary plastic filaments.
Sustainability can also be achieved by using biodegradable filaments, such as PVA, or Polyvinyl Alcohol, a soft and biodegradable polymer that is highly sensitive to moisture. When exposed to water, PVA will dissolve, which makes it a very useful support structure material for 3D printing. When printing extremely complex shapes or ones with partially enclosed cavities, PVA supports can be used and easily removed by dissolving in warm water. Standard supports may have been difficult to print or remove in these situations. PVA can also be used as a model material if there is a need to make quick prototypes, with the end-goal of not wasting or polluting, such as in the case of ordinary plastic filaments.
- A more efficient design
3D printers can make parts with shapes and features unachievable with other manufacturing methods, having the ability to redesign a product, so as to make it more efficient and less resource-consuming. This way, various products do not have to be made using different parts, having the ability to be printed wholly, reducing time, material and labour.
- Less Material Usage
One of the main principles of Additive Manufacturing is the optimization of the usage of material used for the making of a final product. Placing the material precisely where it is needed for the creation of a component is much more efficient than carving a block of material, generating scraps.
- Repairability and the Production of Spare Components
3D printers have the ability to cheaply create new parts for out-of-production or unique equipment, eliminating the need for raw materials, and, consequently, the wasting of energy. The lifespan of older machinery can thus be prolonged by engineers, who, with the help of Computer Aided Design (CAD), can develop the tools necessary for any necessary repairs.
- Local Production of Components
3D printers are available in different sizes, but most of them can fit in an office, thus offering the possibility of production of prototypes and any other products locally, as opposed to shipping them from manufacturies that can be located anywhere on the planet. This way, the undoubtedly negative environmental impact, as well as the shipping costs of the aeroplanes, trucks or ships is minimized.
- Elimination of the Need for a Large Inventory
Additive Manufacturing allows the production of small batches, instead of the overstocking of components produced by other methods, some of which may never be used. This solution has seen implementation by some eyewear brands, that develop their products according to every customer’s preference on demand, eliminating the economic incentive of any other means of production for a large stock.
- Streamline Manufacturing
Another one of the advantages of Additive Manufacturing is that these machines require fewer tools and processes than traditional manufacturing. Though some methods require post-processing, AM usually needs very little labour between the digital design and production. This is why 3D printing has begun to be used to make prosthetics adapted to the needs of every patient, and also medical models, without the need of a factory.
- Smaller and Quieter Factories With a 3D printer being able to replace many pieces of traditional manufacturing needed for the production of a variety of parts, while also needing less materials, the environmental impact of the process of developing components is much smaller, also occupying less space, a valuable resource in urban environments. Noise pollution is also reduced, as 3D printers generate much less noise than traditional manufacturing equipment.
- https://www.simplify3d.com/support/materials-guide/pva/
- https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Paolo-Minetola/publication/316465179_About_the_Use_of_Recycled_or_Biodegradable_Filaments_for_Sustainability_of_3D_Printing/links/5d305d96458515c11c39ad96/About-the-Use-of-Recycled-or-Biodegradable-Filaments-for-Sustainability-of-3D-Printing.pdf?_sg%5B0%5D=started_experiment_milestone&origin=journalDetail
- https://all3dp.com/4/7-ways-3d-printing-helps-you-become-eco-friendly/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bioplastic
- https://www.sculpteo.com/en/3d-learning-hub/3d-printing-materials-guide/3d-printing-bioplastics/
- https://all3dp.com/2/best-biodegradable-3d-printer-filament/
- https://pure.rug.nl/ws/portalfiles/portal/227878802/Macromolecular_Rapid_Communications_2020_Voet_Sustainable_Photopolymers_in_3D_Printing_A_Review_on_Biobased_.pdf
- https://www.sculpteo.com/en/materials/jet-fusion-material/pa11-hp/
- https://www.aha.org/aha-center-health-innovation-market-scan/2022-06-07-3-ways-3d-printing-revolutionizing-health-care
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2351978918301367
- https://pure.rug.nl/ws/portalfiles/portal/227878802/Macromolecular_Rapid_Communications_2020_Voet_Sustainable_Photopolymers_in_3D_Printing_A_Review_on_Biobased_.pdf
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2351978918301367?ref=pdf_download&fr=RR-2&rr=777d5f9a8c495b6e
Ways 3D Printing Helps With Sustainability
Nothing can be perfect
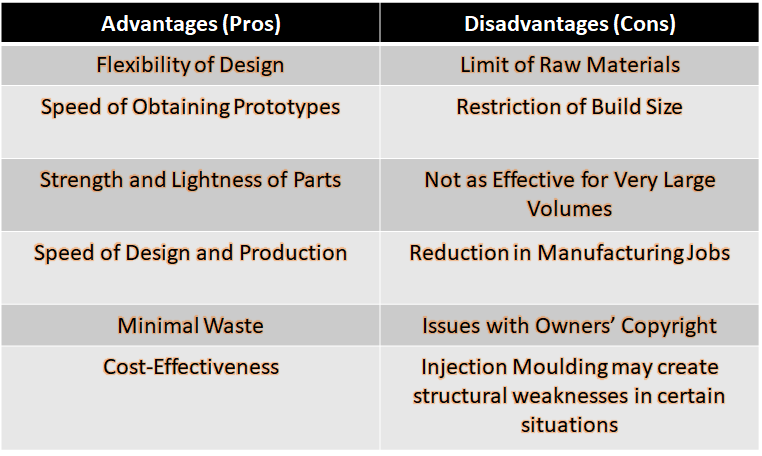
Advantages and Disadvantages of Additive Manufacturing
Summary and Conclusions
Additive Manufacturing allows the production of complex architectures in a more efficient and straightforward manner than traditional methods. This type of production presents further advantages by being able to provide attractive scenarios for sustainable production either through the use of waste material or through the adoption of biodegradable materials. With the dawn of the Information Age, anyone who has an idea that could prove to be beneficial to the sustainable development of humankind may undertake a goal that, years ago could seem impossible without considerable financial backing, as opposed to today’s ease with which anyone in the world with a willingness to alleviate modern problems can bring their solutions to life.
Though no solution has yet be proven to be perfect, Additive Manufacturing has started to be adopted as a more efficient method in almost every field of study and more. Thus, our lives have only begun to be improved by the wonders of such machines, with ideas that combat climate change, help less able humans through the development of cutting-edge medical equipment or, simply make our lives easier.
A few 3D Printed projects that have already seen implementation
 |
 |
| The Million Waves Project, aiming to turn plastic waste into 3D printed prostheses |
Artificial Reef, a project by the French company XtreeE have installed the world’s first 3D printed artificial coral reef |
 |
 |
| Clean2Antarctica, supporting a zero-waste lifestyle, have constructed large electric vehicles with the help of 3D printers |
Print your City! uses large-format Additive Manufacturing to transform plastic waste into city furniture |
Bibliography
Proiect realizat de:
Bocai Vlad
Suliman Emre
Profesor îndrumător:
Prof. Nițu Alina